Chlorophyll fluorescence (ChF) can detect individual and multiple nutrient deficiencies simultaneously. The method involves non-destructive, precise, real-time measurements. A species-specific approach is necessary when developing ChF-based technology to detect multiple nutrient deficiencies. The main aim of agricultural practices is to optimize conditions and resources essential to maintaining productivity. Instead of determining the levels of a… Continue reading…
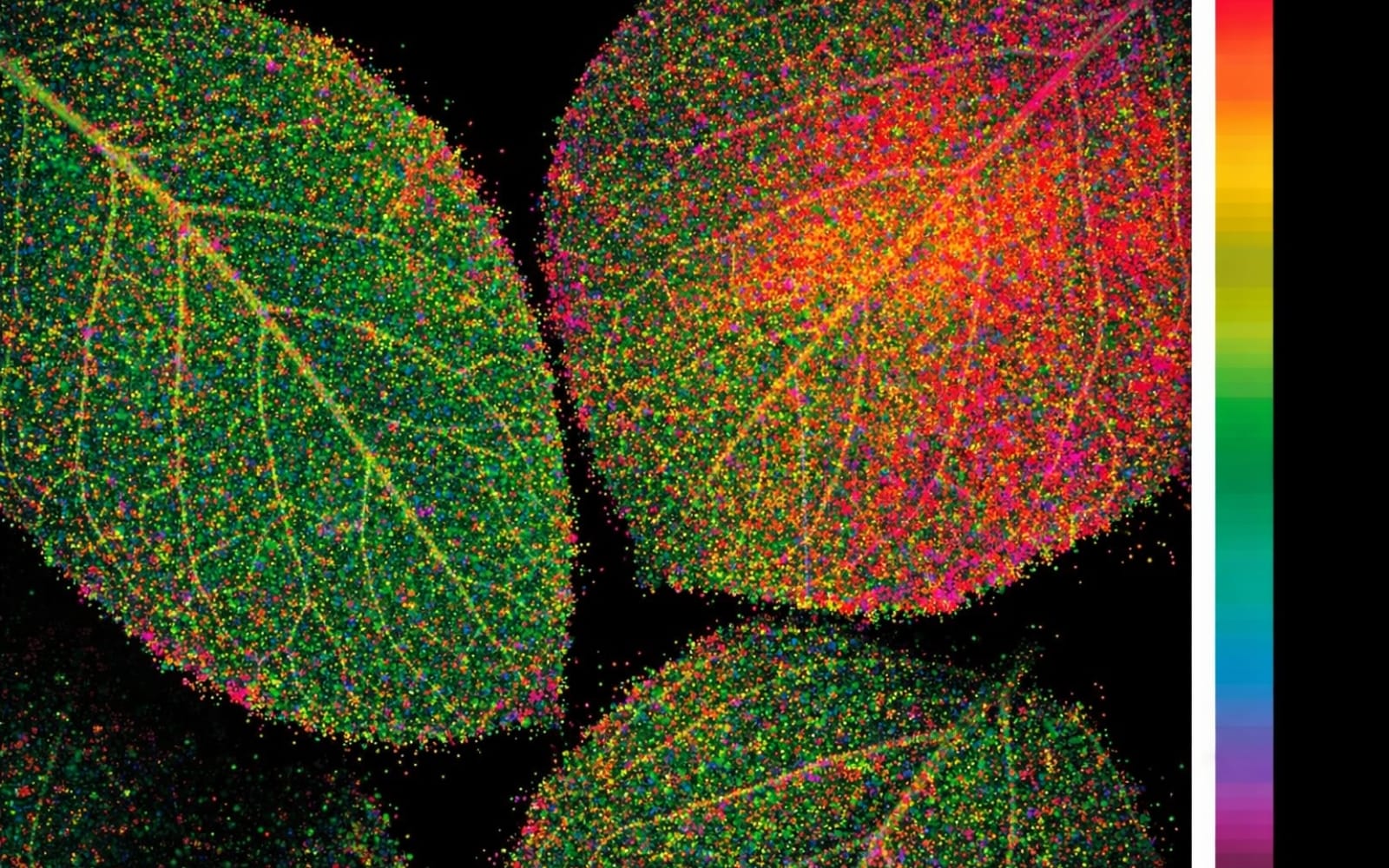
How Light Fluorescence Ratios Help Detect Plant Stress Before Symptoms Appear
Plant leaves fluoresce red, far-red, blue, and green under varying wavelengths of light. Chlorophyll fluorescence-based ratios include Fv/Fm and the red-to-far-red ratio. Fluorescence from red, far-red, blue, and green light occurs in response to UV light. Blue-to-red and blue-to-far-red ratios are more sensitive to stress than the chlorophyll fluorescence ratio of red/far-red. Plants do not… Continue reading…