Latest spectroscopy
How Light Fluorescence Ratios Help Detect Plant Stress Before Symptoms Appear
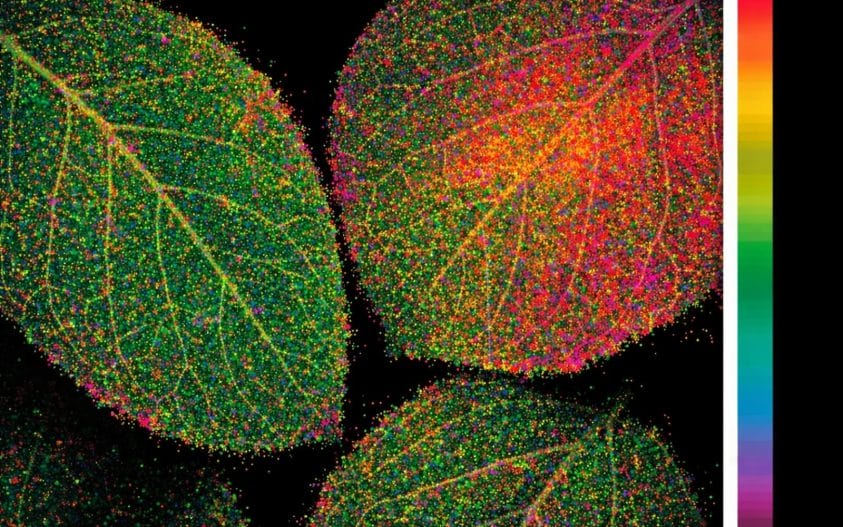
Plant leaves fluoresce red, far-red, blue, and green under varying wavelengths of light. Chlorophyll fluorescence-based ratios include Fv/Fm and the red-to-far-red ratio. Fluorescence from red, far-red, blue, and green light occurs in response to UV light. Blue-to-red and blue-to-far-red ratios are more sensitive to stress than the chlorophyll fluorescence ratio of red/far-red. Plants do not… Continue reading…

Additional reading
How Plant Science is Advancing Sustainability in Agriculture
Sustainability in Agriculture covers economic profits, environmental health, and social equity. Sustainable agriculture involves safeguarding humans, conserving natural resources, and improving the quality and quantity of profitable production throughout the food supply chain. Plant science aims to increase productivity with less inputs, chemicals, and water and more reliance on natural processes and onsite resources. Plant… Continue reading…
What is Senescence in Trees and Why Is It Important?
Senescence occurs at the cell, tissue, organs, and individual levels. Organ senescence is consequential in trees as it helps “recycle materials” within an individual tree to maintain function and productivity. Organ and whole tree senescence are also crucial for nutrient cycling, wildlife diversity, and forest productivity. Senescence is an integral part of all living organisms,… Continue reading…
Can Spectroscopy Predict Leaf Traits Across Ecosystems?
Yes, but with caveats. Leaf traits are used to understand plant growth, functional diversity, and ecosystem processes. Several traits spanning functional groups and geographies can be easily predicted using general models based on spectral data. However, all models cannot have global applications without validation, as the relationship between traits and spectral data is not the… Continue reading…
Invisible Signals 2024: How To Use Plant Spectroscopy To Reveal Disease & Enhance Plant Health
Request a Quote | Schedule a Demo To view the full slide deck, click here. Video Description Did you miss our exclusive webinar on the latest advancements in Leaf Spectroscopy for 2024 featuring the Spectravue Leaf Spectrometer? Don’t worry. You can watch the full recording here! In this webinar, we covered: Impact on Plant Health:… Continue reading…
Plant Responses to Heat Stress
Heat stress affects crop development, growth, and productivity. Plants have adaptive responses for either avoidance or tolerance of heat stress. The plant responds to heat, which can be molecular, biochemical, cellular, physiological, and morphological, and is being used by scientists to develop new cultivars for the future. The increase in temperature due to climate change… Continue reading…
How to Measure 7 Types of Stress in Plants Using Leaf Spectroscopy
Leaf Spectroscopy can measure seven common stresses that crops encounter. The crop leaf stressors are drought, nutrient deficiency, temperature, pests, diseases, salinity, and herbicides. Spectral changes due to physiological, anatomical, and chemical alterations triggered by stress are used in its measurement. Various methods are visual, multispectral, hyperspectral, thermal imaging, and light interaction. Yield depends on… Continue reading…